Table of content
-

Non-Resident Nepali (NRN) Laws in Nepal: Key Highlights
01. Introduction
This article highlights basic rights recognized by the Nepalese Law for Non-Resident Nepali (“NRN”). Article mainly covers following details:
-
Governing Law Related to NRN
-
Process of receiving the NRN Card and NRN Citizenship
-
Rights Granted under NRN Card and NRN Citizenship
02. Governing law related to NRN
Following are the law governing NRN in Nepal:
01. The Constitution of Nepal;
02. Non-Resident Nepali Act, 2008; and Non-Resident Nepali Regulations, 2009
03. Nepal Citizenship Act, 2006;
04. Foreign Investment and Transfer of Technology Act, 2019 (“FITTA”); and
05. Immigration Act, 1992; and Immigration Regulations, 1994.
03. Non-resident Nepali Definition
Non-Resident Nepali Act, 2008 qualifies (a) A Foreign Citizen of Nepalese Origin and (b) Nepalese citizen residing abroad for more than 2 years, as NRN. It excludes Non-Resident Nepali residing on SAARC region.
01. A Foreign Citizen of Nepalese Origin
A foreign citizen of Nepalese origin is defined as an individual who him/herself or whose father, mother grandfather or grandmother was a citizen of Nepal at any time and has subsequently acquired the citizenship of any other foreign country other than a member country of the South Asian Association of Regional Co-operation (SAARC).
02. Nepalese citizens residing abroad.
Nepali citizen residing abroad means any person who is residing in any foreign country for at least 2 (two) years and is involved in any profession, occupation, business and employment except in SAARC region. The definition of NRN also excludes any person who is serving in a diplomatic mission or consulate situated in a foreign country under the assignment of the government of Nepal or who is studying in an academic institution situated in a foreign country.
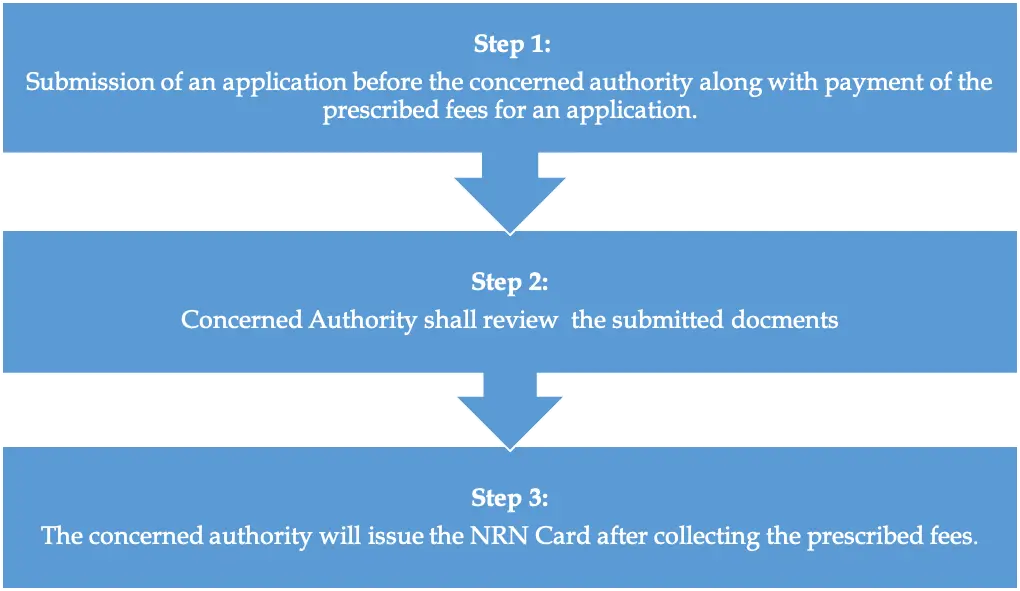
04. Process of receiving NRN Card
Any non-resident Nepali or his/her family if intends to register his/her name as in the status of non-resident Nepali, shall submit the application before the (i) Nepali Embassy Located at Foreign Jurisdiction or (ii) The Secretary of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs ("MOFA") for Nepal. Upon registering the Name and maintaining the record, an NRN Card shall be issued to such NRN.
Process of receiving the NRN Card are as follows:
05. Required Documents for recording and obtaining NRN Card
Required Documents to be fulfilled by the Foreign Citizen of Nepalese Origin are:
a.. A duly filled-in application form
b.. Naturalization Certificate and its copy provided by the respective country
c. Copy of Valid Passport Biographic Data Page issued by the respective country
d. Citizenship Certificate and a copy of it as proof of Nepali Origin for the person who earlier held Nepali citizenship)
e. Copy of Citizenship Certificate of Father/Mother/Grandfather/Grandmother or any other document that proves their Nepali Nationality and evidence of relationship
f. Document/proof of any profession/ business/occupation in the country of current nationality.
g. Two recently taken passport-size photos (for the application form)
h. Two recent auto-size photos (for the identity card)
i. Application and Card Fee
Required Documents to be fulfilled by the Nepalese citizens residing abroad are:
a. A duly filled-in application form.
b. Nepali Citizenship Certificate and its copy.
c. Nepali Passport and Copy of Valid Passport Biographic Data Page.
d. Documents related to business/profession in the current country of residence
e. Document/proof of employment in the current country of residence.
f. A recent passport-size photo
g. Two recent auto-size photos (for the identity card)
h. Application and Card Fee
06. Validity of NRN Card
| Non-Resident Nepali | Validity of NRN Identity Card |
|---|---|
| For Foreign Citizen of Nepalese Origin | Valid for a maximum of ten years |
| For Nepalese Citizen Residing Abroad |
Valid for two years (The duration can be extended if the foreign state authorities allow the Nepali citizen residing aborad to stay overseas for more than two years) |
07. Visa facilities available to NRN
Generally, Foreign Citizens of Nepalese Origins receive two distinct types of visas.
a. Initially, they are granted a Tourist Visa upon their arrival, and
b. Subsequently, they are granted an NRN Visa after they make an application for an extension of visa before the Department of Immigration Management ("DOIM").
NRN visa until the NRN Card remains valid. NRN Visa is issued for a Maximum of 10 (ten) years subject to the validity of the NRN Identity Card. The documents required for obtaining an NRN visa are as follows:
a. An online visa application form is available on the website of DOIM;
b. NRN ID Card (original and photocopy); and
c. Latest Nepalese visa and valid passport.
08. The rights of NRNs relating to property.
Any foreign citizen of Nepalese origin may acquire the land or other property in order to reside within Nepal for him/herself or his/her own family. They may acquire the land or other property by the following ways:
8.1 By virtue of purchase
Any foreign citizen of Nepali origin may purchase any land in any one of the regions and not exceeding the following area, in order to reside within Nepal for him/herself or his/her own family in Nepal:-
| S.N. | Place of Land | Area |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Kathmandu Valley | Max. 2 (Two) Ropani |
| 2. | Municipalities of the Terai district | Max. 8 (Eight) Katha |
| 3. |
Other municipalities except in Kathmandu Valley and Terai district | Max. 4 (Four) Ropani |
| 4. | Village Development Committees of the Terai district | Max. 1 (One) Bigha |
| 5. | Other than the places mentioned above | Max. 10 (Ten) Ropani |
Note: The above-given land ceiling does not apply to those Foreign Citizens of Nepalese Origin who had acquired land while being Nepali citizens.
8.2. By virtue of inheritance
In general, foreigners would require the approval of the Government of Nepal in order to inherit ancestral immovable property. However, Foreign Citizens of Nepalese Origin can inherit the ancestral property from both Nepalese and Foreign Citizens of Nepalese Origin without obtaining such approval. Furthermore, a Foreign Citizen of Nepalese Origin is required to have an NRN Card to inherit the immovable property devolved to him/her.
8.3 By virtue of Investment
Like any other foreign investor, FITTA 2019 permits NRNs to make investment in Nepal. The detailed analysis has been addressed on below paragraph 9 of the article.
09. Foreign Investment into Nepal by NRN.
Foreign Investment and Transfer of Technology Act, 2075 (2019) (“FITTA 2019”) has classified investment done by NRN as a “Foreign Investment” and requires investment approval. An NRN individual is permitted to make foreign investments either by himself/herself or through a foreign company in which s/he owns more than 50 (fifty) percent shares. After investment NRN has right to repatriate the investment from Nepal. This article provides details regarding the FDI approval process in Nepal:
https://lawbhandari.com/publication/foreign-direct-investment-(fdi)-approval-process-in-nepal
However, as a matter of practice if NRN individual is doing investment from his property of Nepal and provide the commitment letter that he/she shall not be taking the profit to foreign country then on such commitment NRN are allowed to invest in Nepal without taking FDI approval.
10. Non-resident Nepalese citizenship
10.1 Nepal Government through the 3rd amendment of the Nepal Citizenship Regulation, 2006 (2063) has permitted the Non-Resident Nepali to obtain the NRN Citizenship.
Non-resident Nepali having the foreign citizenship has right to receive the NRN citizenship by providing economic, social and cultural rights expect political rights. The 3rd Amendment has granted every citizenship rights expect the political rights.
Any person who has acquired citizenship of a foreign country may obtain Non-resident Nepalese citizenship ("NRN Citizenship") upon the following Conditions:
a. who has resided in a country other than a member state of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC);
b. who or whose father or mother, grandfather or grandmother was previously a citizen of Nepal by descent or birth.
Applicant intending to apply for NRN Citizenship have to prove either their father, mother, grandfather or grandmother at some point was a citizen of Nepal and later acquired citizenship of a foreign country other than a member of the SAARC Nation.
10.2 Process of obtaining NRN citizenship.
Any non-resident Nepali or his/her family if intends to obtain NRN citizenship, shall submit the application before the concerned authority.
a. The Concerned authority are:
-
The Chief District Officer of the concerned districts for Nepal
-
Nepalese Embassy or the Consulate General of country of which he or she is citizen or designated jurisdiction to such country
10.2 Process of obtaining the NRN Citizenship:

11. Documents requirements for obtaining the NRN Citizenship:
The following documents are required for obtaining the NRN Citizenship certificate:
a. Recommendation of the ward office to provide NRN Citizenship,
b. Letter of commitment as format provided by the CDO Office,
c. If the applicant had acquired the Nepali Citizenship before, proof of the document related to renunciation of Nepali Citizenship.
d. Citizenship certificate or passport of foreign country,
e. Proof of residence of foreign country
f. Close relatives (any 2) of the applicant should visit the CDO Office. In absence of close relatives any Nepali Citizens who know the applicant should be present.
g. Document reflecting either their father, mother, grandfather or grandmother at some point was a citizen of Nepal and later acquired citizenship of a foreign country.
*Note: The CDO has right to take help of the police authority to investigate in case of any doubt on the information provided by the applicant.
Looking for best NRN lawyer, Please follow the link.
Disclaimer: Bhandari Law and Partners is one of the leading law firm in Nepal with team of best professional lawyers. This article published on website of the law firm is just for information purpose only. It shall not be taken as the legal advice, advertisement, personal communication, solicitation or inducement. Bhandari Law and Partners or any of the team members of the firm shall not be liable for the consequence arising of the information provided. As the factual situation may be different on your case, thereof if you need further legal advice on the subject matter, please Contact Us.
Related Professionals:
Frequently Asked Question
For quick legal assistance:
You can directly call to our legal expert: +977-9808811027
Even can call or drop a text through What’s app , Viber, Telegram and We Chat at the same number.
Also can do email on : info@lawbhandari.com
contact us
Phone :,
,Connect with our professional lawyers in Nepal :
Follow Our Law Firm on Social Media :