Table of content
-

Frequently asked Questions (FAQ) on Company registration in Nepal by foreign investor
01. What is the minimum threshold of investment while establishing FDI business in Nepal?
The minimum investment threshold for FDI Company is 2,00,00,000/- (approximately USD 145,000). However, pursuant to the Nepal Gazette notification dated October 2, 2023, the minimum investment threshold has been waived for companies operating in Information Technology (IT) Sector.
02. What are the areas restricted for foreign investment in Nepal?
The restricted industries for foreign investment are as follows:
-
Poultry farming, fisheries, bee-keeping, fruits, vegetables, oil seeds, pulse seeds, milk industry and other sectors of primary agro-production,
-
Cottage and small industries,
-
Personal service business (hair cutting, tailoring, driving etc.),
-
Industries manufacturing arms, ammunition, bullets and shell, gunpowder or explosives, and nuclear, biological and chemical (N.B.C.) weapons; industries producing atomic energy and radio-active materials,
-
Real estate business (excluding construction industries), retail business, internal courier service, local catering service, moneychanger, remittance service,
-
Travel agency, guide involved in tourism, trekking and mountaineering guide, rural tourism including homestay,
-
Business of mass communication media (newspaper, radio, television and online news) and motion picture of national language,
-
Management, account, engineering, legal consultancy service and language training, music training, computer training, and
-
Consultancy services having foreign investment of more than fifty-one percent.
-
Ride sharing having foreign investment of more than Seventy percent.
In case of aircraft operation, training, maintenance and passenger service facility provider industries, foreign investment shall not exceed the following limits:
-
International air services: 80%
-
Domestic air services: 49%
-
Training institution (aviation-related): 95%
-
Maintenance institutions: 95%
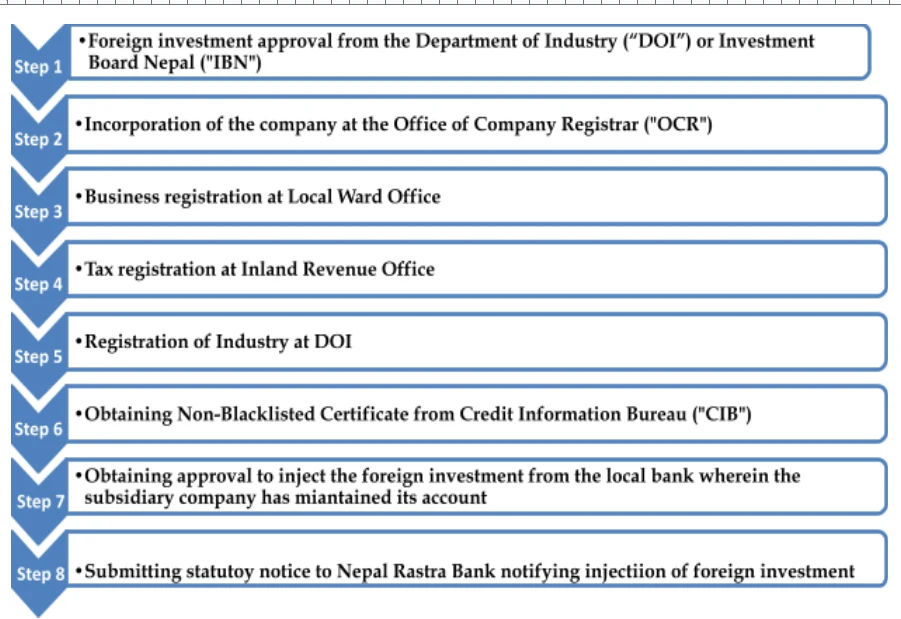
03. What is the process for the establishment of FDI Company in Nepal?
The process for establishing an FDI company in Nepal involves the following steps:
04. What is the list of documents required for establishing FDI company in Nepal?
Following documents and information are required depending on whether the investor is a legal entity or an individual:
a. Legal Entity as an Investor
-
Notarized Copy of Company Registration Certificate, Memorandum of Association, and Article of Association
-
Notarized Copy of Passport of Director and Shareholders of Company
-
Signed Company Profile of the investing company
-
Notarized Copy of passport/citizenship of investor’s authorized representative
-
Proposed Name of company and address of company in Nepal
-
Proposed Investment Amount
-
Project Report for the operation of a local subsidiary company
-
Financial Credibility Certificate (FCC) of Investor issued by a local bank in the home country
-
Notarized latest audit report of Investor Company
-
Resolution of the Investor for investing in Nepal
-
Power of attorney authorizing individuals to complete the approval and registration process on behalf of the Investor
-
Notarized Joint Venture Agreement in case of two or more than two investor
-
Additionally, if the investor company is owned by another company, then the documents of the ultimate beneficiary company are also required
b. For Individual as an Investor
-
Notarized Copy of Passport of Individual Investor/s
-
Bio Data in case of an Individual Investor/s
-
Proposed Name of Company and address of company in Nepal
-
Proposed Investment Amount
-
Project Report for the operation of a local subsidiary company
-
Financial Credibility Certificate (FCC) of Investor issued by a local bank in the home country
-
Power of attorney authorizing individuals to complete the approval and registration process on behalf of the Investor
-
Notarized Joint Venture Agreement in case of two or more than two investor
Based on the provided documents, the project report and other necessary filings are drafted and shared with the client by email for execution. The client is required to print, execute, and notarize the necessary documents and courier the originals to Nepal.
Upon receipt of the executed documents, the FDI application is filed with the Department of Industry (DOI). For certain industries, approval is granted through the Automatic Route, which allows for expedited processing once the application and required documents are filed online.
05. Which is the authority granting the approval for foreign investment in Nepal?
Department of Industry is the primary authority responsible for granting approval for foreign investment in Nepal. However, Investment Board of Nepal (IBN) is responsible for granting approval for the FDI projects exceeding NPR. 6 billion and for managing the endorsement and execution of energy projects with a capacity of 200 megawatts or more.
06. How long does it take to get approval for foreign investment in Nepal?
The timeline for getting approval depends upon sector of investment. Certain sectors fall under the automatic approval route where investors receive the FDI approval certificate immediately upon submitting the application through the online system operated by DOI. For sectors not under the automatic approval route, approval generally takes 2 to 4 weeks or longer, depending on the nature of the investment and the review requirements of the concerned authorities.
07. What sectors of foreign investment are allowed through the automatic route?
The following sectors and subsectors are eligible for foreign investment under the automatic route:
| S.N. | Sector | Sub-Sectors |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Energy Based Industries | 1. Energy production from wind 2. Energy production from solar power 3. Energy production from biomass 4. Energy Production from other Resources 5. Manufacturing of machine/equipment used for wind energy plant 6. Manufacturing of machine/equipment used for solar energy plant 7. Manufacturing of machine/equipment used for biomass energy plant 8. Energy production from bio-gas 9. Energy production from cogeneration in sugar industries 10. Feasibility study of energy |
| 2 | Agriculture and Forest Products Based Industries | 1. Fruits processing 2. Vegetables processing 3. Establishment and operation of green house 4. Silk processing 5. Tea processing 6. Coffee processing 7. Herbs processing 8. Rubber processing 9. Cold Store (For Storing Local Fruits and Vegetables) 10. Natural fibers products processing 11. Paper, resins and other non-timber based industries 12. Producing plants through new technology (Tissue Culture & others) 13. Cotton processing |
| 3 | Infrastructure Industries | 1. Vehicles parking station/house 2. Export processing zone 3. Water purification (waste water treatment plant) 4. Film city Construction 5. Film studio Construction 6. Construction and Operation of Warehouses |
| 4 | Tourism Industries | 1. Motel, Hotel, Resort, Bar and Restaurant 2. Fun park 3. Water park 4. Convention and Sports Tourism |
| 5 | ICT Industries | 1. Technology park 2. IT park 3. Biotech park 4. Software development 5. Data processing 6. Digital mapping 7. Business process outsourcing (BPO) 8. Knowledge process outsourcing (KPO) 9. Data center 10. Data mining 11. Cloud computing 12. Web portal 13. Web designing service |
| 6 | Service Industries | 1. Mechanical workshop 2. Construction business 3. Hospitals 4. Nursing homes 5. Polyclinics 6. Operation of Rehabilitation Centre 7. Physiotherapy clinics 8. Ayurveda and other alternative hospitals 9. Sports services 10. Swimming pool 11. Solid waste collection and sanitation 12. Recycling of waste 13. Veterinary services 14. Health checkup (X-Ray, CT Scan, MRI, Ultrasound, or similar services) 15. Health checkup laboratories 16. International Courier services |
| 7 | Manufacturing Industries | 1. Manufacturing of Fodder For Livestock and Fish 2. Meat Processing and Packaging of Livestock and Fish 3. Manufacturing of Oil or Fat from Basic Raw Materials 4. Manufacturing of Starch or Glucose 5. Manufacturing of Bakery Products 6. Manufacturing of Confectionary and Biscuit 7. Manufacturing of Sugar 8. Manufacturing of Beverages (Non-Alcoholic) 9. Manufacturing of Textile, Garment And Apparel (Using new and Re-used materials) 10. Manufacturing of Electronic Home Appliances 11. Manufacturing of Goods Using Plastic Or Rubber 12. Manufacturing of Bag, Sack, Suitcase, Trolley Bag or Other Similar Bag for Carrying Things 13. Manufacturing of Wooden Goods Other than Traditional and Cultural Art Based 14. Manufacturing of Toiletries Products like Toothpaste, Soap or Shampoo 15. Manufacturing of Products Based on Glass 16. Manufacturing of Cycle, Scooter, Motorcycle and Four Wheeler and accessories used in such vehicle 17. Manufacturing of Electric Lamps, Switch, Meter, Fuse, Wiring Cable, Compressor, and Similar Products 18. Manufacturing of Goods used in Medical, Surgical, Orthopedic Works 19. Manufacturing of Electrical Wire |
08. What are the documents required for getting FDI approval?
The following documents are required to obtain FDI approval:
-
Online Application
-
Color scanned copy of project proposal/report.
-
Color scanned copy of Joint Venture Agreement (in case of more than 1 investior)
-
Scanned copy of Power of Attorney
-
Investor’s Documents
a. For individual
i. Notarized copy of citizenship (Nepali)/Passport (Foreigner)
ii. Bio-data
iii. Notarized copy of Financial Credibility Certificate (FCC) of the foreign investor issued by the bank of home country
b. For Company
i. Notarized copy of Certificate of Incorporation including memorandum of association and article of association
ii. Board decision to invest in Nepal
iii. Shareholders details showing the ultimate beneficiaries
iv. Company profile
Note: Physical copies of the above documents must also be submitted to the concerned authority.
09. What is Financial Credibility Certificate (FCC)?
A Financial Credibility Certificate (FCC) is an official document issued by a recognized bank or financial institution confirming that the investor possesses adequate financial resources and credibility to invest in Nepal. It serves as proof of the investor’s financial soundness and reliability and is required when seeking approval for foreign investment in Nepal.
10. What is the tentative time line for completing registration of FDI Company?
Once the FDI approval is secured, it generally takes around 3 months for the complete registration of FDI Company.
11. What is the timeline for injecting the committed investment amount?
The Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA) specifies 3 stages for the injection of foreign investment amount:
| Stages | Details | Percentage of Injection of Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Stage I | Within 1 year of receiving the investment approval: | Depends on the amount of investment |
| Minimum investment amount i.e. NPR 20 Million | 25% | |
| 20 to 250 million NPR | 15% | |
| 250 million NPR to 1000 Million | 10% | |
| Stage II | When the company starts production or does start the commercial transaction | Up to 70% of the investment amount |
| Stage III | After 2 years of production or commencement of transaction | Remaining 30% of the investment amount |
12. Do investor/shareholders of the company need to visit Nepal in person during any part of the process?
Yes. At least one investor must be physically present in Nepal after the company registration to:
-
Obtain a personal Permanent Account Number (PAN) from the tax office; and
-
Complete biometric verification for the company’s registration.
Once the business tax certificate is obtained, the company becomes eligible to open a bank account in Nepal. To do so, the representative director must be physically present at the bank to complete KYC procedures and other required formalities.
13. What are the other post registration requirement for FDI Company?
a. Initial Compliance at OCR
After the company is incorporated by the Office of the Company Registrar (OCR), the company within the first three month of incorporation shall provide the information of address, appointment of the auditors and the formation of the Board of Directors in accordance with section 92 and section 184 of the Company Act, 2063 (2006).
b. Inflow Certificate from the Bank
Once the company submits the statutory notice to the Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB) the investors can inject the investment amount to the local bank in company’s bank account. After the Investment amount is injected in the company’s bank account, the bank request for the required documents for the issuance of the Inflow Certificate.
c. Share distribution and Shareholder’s Registry
After the bank provides the inflow certificate, we can distribute the company share to the shareholders and submit the documents to the Office of the Company Registrar (OCR). The OCR issues certified the Share Registry. Share Registry is provided by the OCR as certification to the shares owned by the shareholders.
d. Recording of the Foreign Investment at the NRB
Additionally, after the above compliance are fulfilled is completed, recording must be done of the Foreign Investment amount along with submission of the required documents like Inflow Certificate, Share Registry and other company details. Nepal’s Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act requires foreign investments to be registered with the NRB to ensure they adhere to legal and regulatory frameworks. This helps maintain transparency and accountability.
e. OCR Annual Compliance
Companies are required to convene their first AGM within one year of incorporation, submitting the following documents to the OCR:
-
Details of the AGM, confirming adherence to the Companies Act.
-
Audited financial statements and an audit report for the fiscal year.
From the second year onward, AGMs must be held annually, with annual reports submitted to the OCR within six months of the fiscal year-end (typically June or July).
f. Labour Law Compliance
Compliance with Nepal’s labor laws requires the preparation of a company handbook and the execution of employment agreements with staff to ensure adherence to employment regulations. The Company further need to be enrolled in Social Security Fund which is contribution based social security scheme.
g. Industry Operation and Extension
FDI companies must commence operations within one year of industry registration with the Department of Industry. Prior to commencing operations, at least 70% of the authorized capital must be injected. The issuance of the first invoice marks the start of operations, and companies must notify the Department of Industry within 30 days of this event. Non-compliance may result in fines.
If operations cannot commence within one year, companies must apply for an extension at least one month prior to the expiry of the industry registration. And Industry Operation Annual Report has to be submitted every year after the industry commencement fiscal year.
14. What should be considered when injecting to the investment amount into the company’s bank account?
Key Requirements include:
-
Funds must be transferred via SWIFT from the investor’s personal bank account maintained outside Nepal
-
The SWIFT transfer message (remark) must clearly state: “Foreign Investment”
15. Is a local Director necessary ?
No. A local director is not mandatory under Nepali law.
16. Is a physical address required for registration, or will a virtual address suffice?
For company registration in Nepal, a physical address is mandatory. The Office of the Company Registrar (OCR) requires the company to provide a verifiable physical location as its registered office address.
17. Can a company bank account be managed from overseas?
While some banks provide e-banking facilities for viewing balances and limited transactions, practical operation of the account (e.g., signing cheques, withdrawing, or authorizing payments) requires a local authorized signatory. Hence, appointing a trusted Nepali representative with Board authorization is recommended for efficient operation.
18. Can the investment be transferred from another person’s or family member’s or relative’s account?
No. The investment amount must be transferred directly from the investor’s personal bank account located outside Nepal.
19. In case of joint investor, can one investor inject the entire investment amount?
No. Each party in Joint Venture (JV) must inject their respective proportion of investment as committed in the JV agreement.
20. When and for how long can we apply for the business visa?
After the incorporation of a company in Nepal, a foreign investor or their representative of the investing corporate entity becomes eligible to apply for a Business Visa. The investor initially enters Nepal on a tourist visa, which is later converted into a Business Visa. For the first time, a Business Visa is generally granted for a period of up to three months. This initial period comes with certain conditions, such as the registration of the industry and demonstration of progress in establishing business operations. Within these three months, the investor is expected to complete necessary registrations and show tangible steps toward setting up the enterprise.
Once the investor injects the committed investment capital into the company, the Business Visa can be extended beyond the initial period. Normally, such extensions are granted for one year at a time, provided that the investment has been made and properly recorded. For the first application, the investor must personally visit the Department of Immigration to obtain the visa.
21. When is the financial year end for the companies in Nepal?
In Nepal, the financial year starts on Shrawan 1 and ends on Ashad 31 of the following year according to the Nepali (Bikram Sambat) calendar. This roughly corresponds to mid-July to mid-July in the English calendar.
22. What is the corporate tax rate and dividend reduction rate?
The current corporate tax rate is 25% of the net profit. The dividend is 5% applicable after the deduction of corporate tax.
23. Does the person registered with the company have to be a director, or can they be a shareholder only?
Shareholders may remain passive and are not required to act as directors. Directors are appointed by the shareholders to manage daily affairs. It is legally permissible for a person to be a shareholder only, without being appointed as a director.
24. Can day-to-day operations be managed by an authorized representative instead?
Yes. The company may appoint a Nepali authorized representative by Board resolution or power of attorney. Such a representative may act as the operational head, handle banking, licensing compliance, and government relations on behalf of the company.
25. When can we repatriate the profit?
Once the company has fulfilled all financial and tax obligations, profits and capital may be repatriated in the same currency as the initial investment or any other convertible currency approved by the NRB. However, repatriation is strictly prohibited within the first year of investment.
26. After registration when shall be begin the operation of the company? Can we apply for extension?
FDI companies must commence operations within one year of industry registration with the Department of Industry. Prior to commencing operations, at least 70% of the authorized capital must be injected. The issuance of the first invoice marks the start of operations, and companies must notify the Department of Industry within 30 days of this event. Non-compliance may result in fines.
If operations cannot commence within one year, companies must apply for an extension at least one month prior to the expiry of the industry registration. And Industry Operation Annual Report has to be submitted every year after the industry commencement fiscal year.
Related Professionals:
Frequently Asked Question
For quick legal assistance:
You can directly call to our legal expert: +977-9808811027
Even can call or drop a text through What’s app , Viber, Telegram and We Chat at the same number.
Also can do email on : info@lawbhandari.com
contact us
Phone :,
,Connect with our professional lawyers in Nepal :
Follow Our Law Firm on Social Media :